Due diligence is crucial in Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A), as it evaluates a company’s financials, operations, and risks to enable sound decision-making.
In the first quarter of 2024 alone, 189 M&A deals involving UK companies were completed, with monthly transactions ranging from 58 to 290 between January 2020 and March 2024.
At Mergers Acquisitions UK, we understand the growing significance of M&A, providing comprehensive due diligence services to help clients navigate complex transactions. In this article, we’ll explore the key elements of M&A due diligence, all the different types, and the processes that help mitigate risks and maximise value in business growth strategies.
What is Due Diligence in Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A)?
Due diligence in M&A is the process of investigating a target company before finalising a transaction. It involves verifying facts, assessing the value of the business, and identifying potential risks. The buyer typically reviews the company’s financials, legal documents, market position, and management structure.
The depth of due diligence depends on the transaction’s complexity and size, ensuring the buyer has a clear understanding of the company’s value and liabilities before proceeding with the deal. This process is an important way of ascertaining risk exposures and statements made by the seller about the transaction.
In the UK, due diligence must comply with regulations like those set by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), ensuring transparency and protection for both parties.
Why is Due Diligence Important before the Mergers and Acquisitions Process?
Due diligence is a vital part of M&A because it helps buyers and sellers to make informed decisions. This process identifies risks, liabilities, and opportunities to ensure a smooth and compliant transaction. In 2021 alone, the global M&A market saw deals worth $5.9 trillion, underscoring the importance of thorough due diligence.
Now, let’s understand the importance of due diligence from buyer’s and seller’s perspectives.
From a Buyer’s Perspective:
Due diligence is important from a buyer’s perspective as it helps them to assess the target company’s true value while uncovering potential risks, and ensuring legal and financial compliance. It provides a comprehensive understanding of the business, allowing buyers to make informed decisions and negotiate favourable terms.
At Mergers Acquisitions UK, we help investors by conducting thorough due diligence, identifying hidden liabilities, evaluating the company’s market position, and ensuring that all relevant documents are accurate. This ensures buyers avoid overpaying as well as minimising risks, leading to more successful transactions.
From a Seller’s Perspective:
Due diligence is crucial for sellers in M&A because it ensures transparency, identifies potential issues early, and helps position the company favourably to maximise its value. It allows the seller to correct problems before negotiations, preventing delays and surprises during the transaction.
A thorough due diligence process can also build trust with buyers. Mergers Acquisitions UK helps sellers by conducting comprehensive due diligence, addressing risks, organising key documents, and presenting the company in its best light to attract potential buyers and secure a fair deal.
What are the Different Types of Mergers and Acquisitions Due Diligence?
In M&A, due diligence covers multiple areas to ensure both buyer and seller fully understand the risks, opportunities, and potential liabilities involved in the transaction. Here are the different types of M&A due diligence:
1. Financial Due Diligence
Financial due diligence is a detailed assessment of the target company’s financial health. The objective is to validate the company’s financial information and ensure its accuracy, identifying any risks, inconsistencies, or financial irregularities that could impact the transaction.
What it includes:
- Analysis of financial statements and tax returns
- Review of assets, liabilities, and debts
- Evaluation of revenue streams and profit margins
- Assessment of cash flow, working capital, and financial forecasts
- Analysis of accounting policies and past financial performance
2. Legal Due Diligence
Legal due diligence is a thorough examination of the target company’s legal standing. This type of due diligence ensures that the company complies with all laws and regulations and identifies any legal risks or obligations that could affect the buyer after the acquisition.
What it includes:
- Review of contracts, agreements, and legal documents
- Evaluation of compliance with local and international regulations
- Investigation of any ongoing or past litigation
- Examination of licences, permits, and intellectual property
- Assessment of potential legal liabilities
3. Operational Due Diligence
Operational due diligence focuses on assessing the internal operations of the target company, including processes, supply chains, and infrastructure. It evaluates the efficiency and scalability of operations and how well the company will integrate into the buyer’s existing operations.
What it includes:
- Analysis of internal processes and workflows
- Review of supply chain, production, and distribution systems
- Evaluation of operational efficiency and capacity
- Examination of IT systems and technology infrastructure
- Assessment of operational risks and synergies with the buyer’s operations
4. Commercial Due Diligence
Commercial due diligence assesses the target company’s position in the market, its competitors, customer base, and growth potential. It helps the buyer understand the business’s prospects and market dynamics that may affect the company’s sustainability.
What it includes:
- Market analysis and industry trends
- Evaluation of the target’s competitive landscape
- Review of the customer base and market share
- Analysis of sales pipelines and revenue growth potential
- Examination of market risks and opportunities for expansion
5. HR and Employee Due Diligence
HR and employee due diligence focuses on the workforce of the target company, examining employee contracts, benefits, compensation structures, and organisational culture. It ensures that the buyer understands employee-related liabilities and opportunities for cultural integration.
What it includes:
- Review of employment contracts and benefits packages
- Evaluation of compensation structures and employee turnover rates
- Examination of labour relations, unions, and employment disputes
- Assessment of key personnel retention and succession planning
- Consideration of cultural alignment and integration risks
6. Tax Due Diligence
Tax due diligence identifies tax risks, liabilities, and compliance issues related to the target company. It includes reviewing tax returns, VAT, and any tax incentives or pending disputes.
It also examines the company’s tax liabilities, past audits, tax strategies, and compliance with UK and EU tax regulations, ensuring there are no outstanding tax liabilities that could affect the deal.
What it includes:
- Review of tax returns and VAT compliance
- Evaluation of the company’s tax liabilities and strategies
- Assessment of past tax audits and disputes
- Examination of tax incentives or credits
- Verification of compliance with local, national, and international tax laws
7. Environmental Due Diligence
Environmental due diligence examines the environmental impact of the target company’s operations. This type of due diligence is particularly important in industries with significant environmental regulations, ensuring that the company complies with environmental laws and does not pose future liabilities.
What it includes:
- Review of environmental permits and compliance records
- Assessment of pollution, waste management, and sustainability practices
- Evaluation of potential liabilities related to environmental damage
- Examination of regulatory risks and pending environmental issues
- Verification of compliance with local and international environmental laws
8. Intellectual Property (IP) Due Diligence
IP due diligence focuses on the target company’s intellectual property assets, ensuring that all patents, trademarks, copyrights, and other IPs are legally owned and protected. It helps the buyer understand the value and risks associated with these assets.
What it includes:
- Review of patents, trademarks, copyrights, and other IP assets
- Assessment of IP ownership and transferability
- Examination of IP-related litigation or disputes
- Evaluation of the target’s IP strategies and competitive advantage
- Verification of licensing agreements and ongoing R&D activities
The Merger and Acquisition Due Diligence Process
The UK’s M&A due diligence process is structured to ensure compliance with legal, financial, and operational standards. Below is a step-by-step guide to the process:
1. Strategic Planning
The buyer identifies target companies that align with their strategic goals, evaluating potential synergies between businesses. Sellers may need to prepare by restructuring assets or isolating them into a new company for the acquisition. At this stage, both parties consider regulatory requirements and financing options to ensure the transaction can proceed smoothly.
2. The Offer
Key deal terms such as price, structure, and conditions are negotiated, usually through a Letter of Intent or Heads of Agreement. Confidentiality agreements are also signed to protect sensitive business information from being shared with third parties, and exclusivity clauses are often included to secure negotiations.
3. Due Diligence
The buyer conducts an in-depth review of the target company’s financials, legal standing, operational practices, and market position. This process helps uncover any potential liabilities or risks, allowing the buyer to verify the accuracy of the provided information and assess the feasibility of moving forward with the acquisition.
4. Legals
The legal teams of both the buyer and seller draft and negotiate the Sale and Purchase Agreement (SPA), including warranties and indemnities to protect the buyer from post-transaction risks. The SPA formalises the deal terms, adjusting for any findings during due diligence, and involves heavy negotiation to balance the interests of both parties.
5. Completion
Once all terms are agreed upon and legal documents finalised, the closing process occurs. Both parties sign the necessary documents, and any regulatory approvals or clearances are obtained. This step concludes the formal transfer of ownership, marking the completion of the M&A transaction.
6. Post-Closing Integration
After closing, integration begins, which involves aligning the merged companies’ operations, systems, and cultures. Effective communication with employees, suppliers, and stakeholders is crucial to ensure a smooth transition, minimising disruption, and preserving business continuity. Post-closing integration is important to achieving the anticipated synergies.
7. Monitoring & Evaluation
Following the transaction, the buyer conducts post-acquisition audits to assess the success of the integration, ensuring all warranties and obligations are fulfilled.
Continuous monitoring of financial performance and operational effectiveness is essential to evaluate whether the merger is delivering expected value and meeting long-term business objectives.
How long does the M&A Due Diligence Process take?
The M&A due diligence process typically lasts four to six weeks, depending on several key factors:
- Deal Complexity: Simple acquisitions with fewer assets or operations may take less time, while more complex deals involving multiple business units, global operations, or intellectual property rights can require extensive review. Complex transactions may also need input from specialised advisors such as industry experts or technology consultants.
- Size of the Deal: Larger deals involve assessing more assets, employees, and operational components. Financial due diligence on significant cash flows, assets, and debt can take longer as auditors, accountants, and legal teams scrutinise every detail.
- Regulatory Approval: If the deal requires approval from government agencies or competition authorities (especially for mergers between large companies or those in regulated industries like telecom or finance), this can extend the timeline.
- Cross-Border Transactions: International deals introduce added layers of complexity, such as compliance with foreign laws, tax regulations, currency exchange considerations, and political risks. Cross-border due diligence requires time to ensure all international regulations are met.
- Financial Review: A thorough analysis of the target company’s financials is one of the most critical steps. This involves reviewing historical performance, forecasting, asset valuations, and identifying potential liabilities. If discrepancies or red flags are discovered, it can prolong the process.
- Stakeholder Negotiations: Depending on the level of engagement with shareholders, employees, and third-party vendors, negotiation timelines can vary. Shareholder approval, especially in publicly listed companies, may require additional time and meetings.
How much does Due Diligence Cost in the UK?
Due diligence costs for purchasing a business in the UK typically range between 2% to 5% of the transaction price. These costs cover various aspects of the due diligence process, including legal, financial, and operational reviews.
The overall cost depends on the size and complexity of the transaction, with larger or more intricate deals incurring higher fees.
Factors influencing the cost include:
- Deal Size: Larger deals require more comprehensive due diligence, increasing the time and resources needed for financial, legal, and operational assessments.
- Industry: Regulated industries like healthcare, finance, or technology often require specialised legal and financial expertise, which adds to the cost.
- Scope of Due Diligence: A broader scope, such as covering environmental, tax, or intellectual property audits, can increase costs.
- External Advisors: Engaging external advisors such as legal, accounting, and industry specialists contributes significantly to the overall expense.
- Cross-Border Deals: International transactions involve navigating multiple legal and regulatory systems, adding additional layers of complexity and cost.
What are the Financial and Tax Due Diligence Steps in M&A Due Diligence?
For M&A financial and tax due diligence in the UK, here are the required steps:
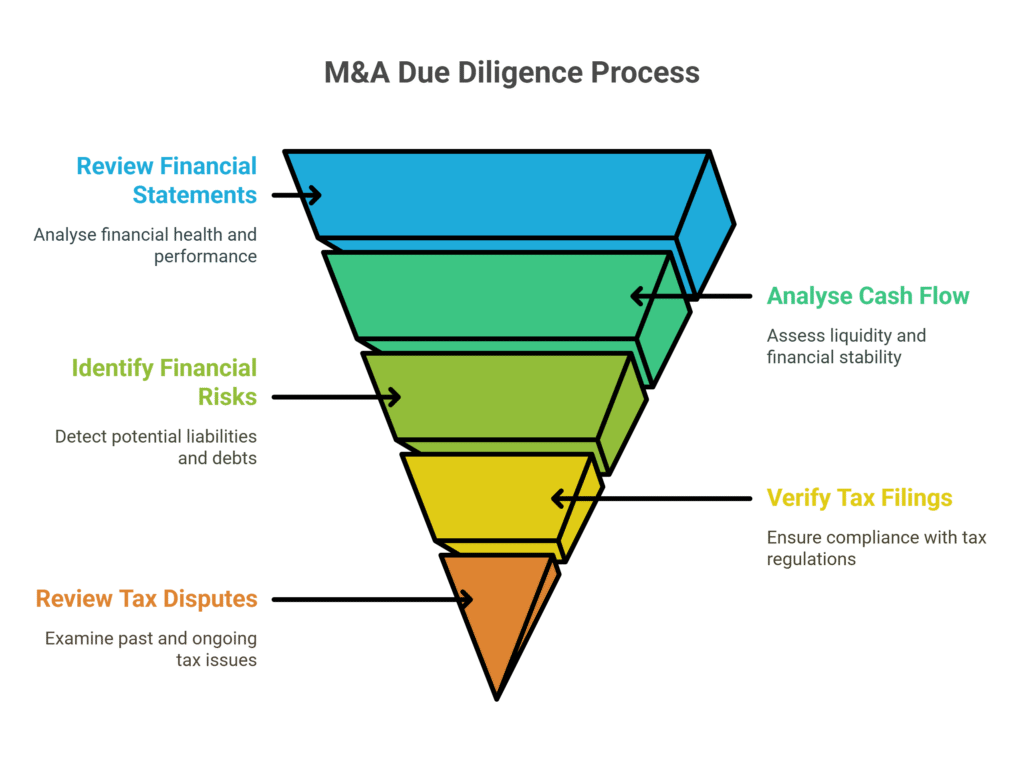
Financial Due Diligence:
- Review financial statements and audits.
- Analyse cash flow, working capital, and outstanding liabilities.
- Assess the target’s revenue sources, profitability, and asset quality.
- Identify any financial risks, including outstanding debt or off-balance sheet liabilities.
Tax Due Diligence:
- Verify tax filings from the past five years, including corporate, VAT, and payroll taxes.
- Review any ongoing or past tax disputes, audits, or penalties.
- Examine compliance with UK tax laws, including transfer pricing and VAT regulations.
How Mergers Acquisitions UK can help you run the Due Diligence Process in Mergers and Acquisitions
Designed to meet UK-specific regulatory standards, Mergers Acquisitions UK transforms the M&A due diligence process by integrating advanced AI-powered tools. This enhances efficiency, security, and compliance.
Here’s how Mergers Acquisitions UK enhances the M&A due diligence process:
- Automated Document Management: Our AI-powered data rooms streamline organisation by categorising financial, legal, and operational documents, reducing manual labour, and ensuring better access.
- Real-Time Collaboration: Instant collaboration enables teams to make faster decisions, improving communication between financial, legal, and operational advisors, and reducing delays.
- AI-Driven Analysis: Our platform analyses contracts, financial statements, and compliance data rapidly, providing key insights and minimising time spent on manual review.
- Data Security: High-level encryption guarantees the protection of sensitive documents, ensuring complete confidentiality.
- UK Compliance: Mergers Acquisitions UK is designed to meet UK-specific regulatory standards, ensuring full legal compliance in the due diligence process.
Efficiency: By automating repetitive tasks, our platform speeds up the process, allowing for faster and more accurate deal closures without sacrificing thoroughness.
